Chronic Wasting Disease: A New Threat To Eurasia’s Deer?
2016, unfortunately, saw the first verified cases of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) outside of its native range in North America, identified back in March in Sogn og Fjordane county, Norway.
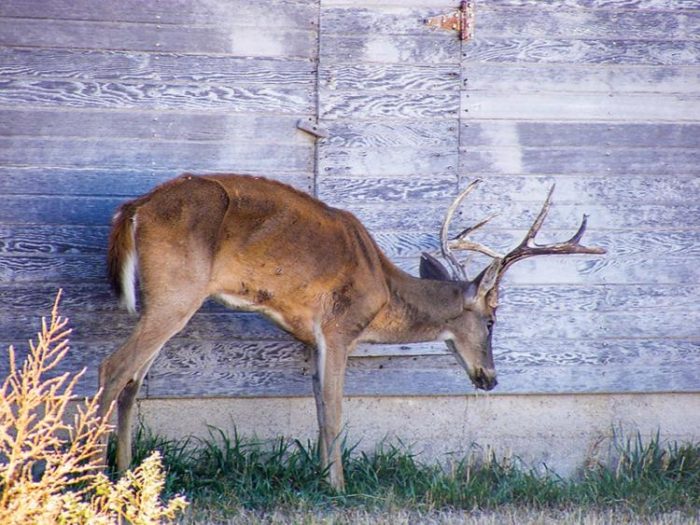 Image: https://huntfish.mdc.mo.gov/hunting-trapping/wildlife-diseases/chronic-wasting-disease-cwd
Image: https://huntfish.mdc.mo.gov/hunting-trapping/wildlife-diseases/chronic-wasting-disease-cwd 2016, unfortunately, saw the first verified cases of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) outside of its native range in North America, identified back in March in Sogn og Fjordane county, Norway. Proceeded by confirmed cases of infection in wild Moose around Selbu, located 300km North of the first case. With the Norwegian Veterinary Institute confirming a fourth case in wild Reindeer soon after. The emergence of this disease in Europe rightfully alarming conservationists who now intend to test some 15,000 cervids (moose, roe deer, red deer and reindeer) in order to assess just how far the disease has spread. The problem, if left unchecked, likely to become one of the most pressing issues in the realms of wildlife management and conservation in the very near future.
CWD is, in every sense of the word, a rather terrible affliction, involving the gradual degeneration of the brain in infected animals. Something which, over time, inevitably results in emaciation, abnormal behavior, loss of bodily functions and, in each case, death. Comparable to Myxomatosis in the drawn-out manner in which it claims its victims and thus deplorable from an ethical standpoint. As are many wildlife diseases. CWD, since it was first detected in a herd of captive Mule Deer in the late 1960’s, now having spread across much of North American, leaving a trail of destruction in its wake. And causing significant damage to both wild deer populations and commercial interests.
What truly sets CWD apart from other diseases, however, is the manner in which it spreads. Passed from animal to animal through the feces, urine or saliva. Something which, in itself, should be easily controlled, if it was not for the diseases resistance to environmental factors. With infected agents released into the environment through the natural bodily process of deer, or the decomposition of a carcass, persisting in the ecosystem for many years. And therefore, easily picked up by additional deer through feeding on infected pasture. Something which presents a significant problem for those wishing to eradicate the infection. It’s spread only hastened by the natural movements of wild deer – known to travel large distances – and the movement of domestic stock or infected materials.
The means by which CWD spreads and the amount of time it can remain in the environment pose a significant problem for wild deer populations in Europe and further afield. Though problematic in North America, the disease has, until now, been restricted to the few species of deer inhabiting the continent. It’s spread hampered by natural geography. Now, however, following its emergence in Europe, CWD has the potential to spread over a much greater geographical area, to a plethora of new ungulate species. With Eurasia, as a whole, boasting the highest diversity of deer species found anywhere in the world. Including vulnerable species such as the Barasingha – native to the Indian Subcontinent. The spread of the disease, though it will likely take many years, almost inevitable absent proper management. More so given the fact that, unlike people, wild deer know no man-made borders.
In a UK context, it would appear that our beloved deer are safe, at least for now. And Britain’s status as an island may well work in our favour if CWD takes hold. It would, however, only take the accidental import of infected animals or contaminated materials to bring the disease to our shores. And I am sure that both conservationists and deer enthusiasts here will be watching events on the continent very closely indeed.
For more information about CWD, you can visit this page by the Chronic Wasting Disease Alliance, and for information on Norweigan affairs relating to it, you can follow this link.




No comments yet.